Conspiracy theories about flat Earth

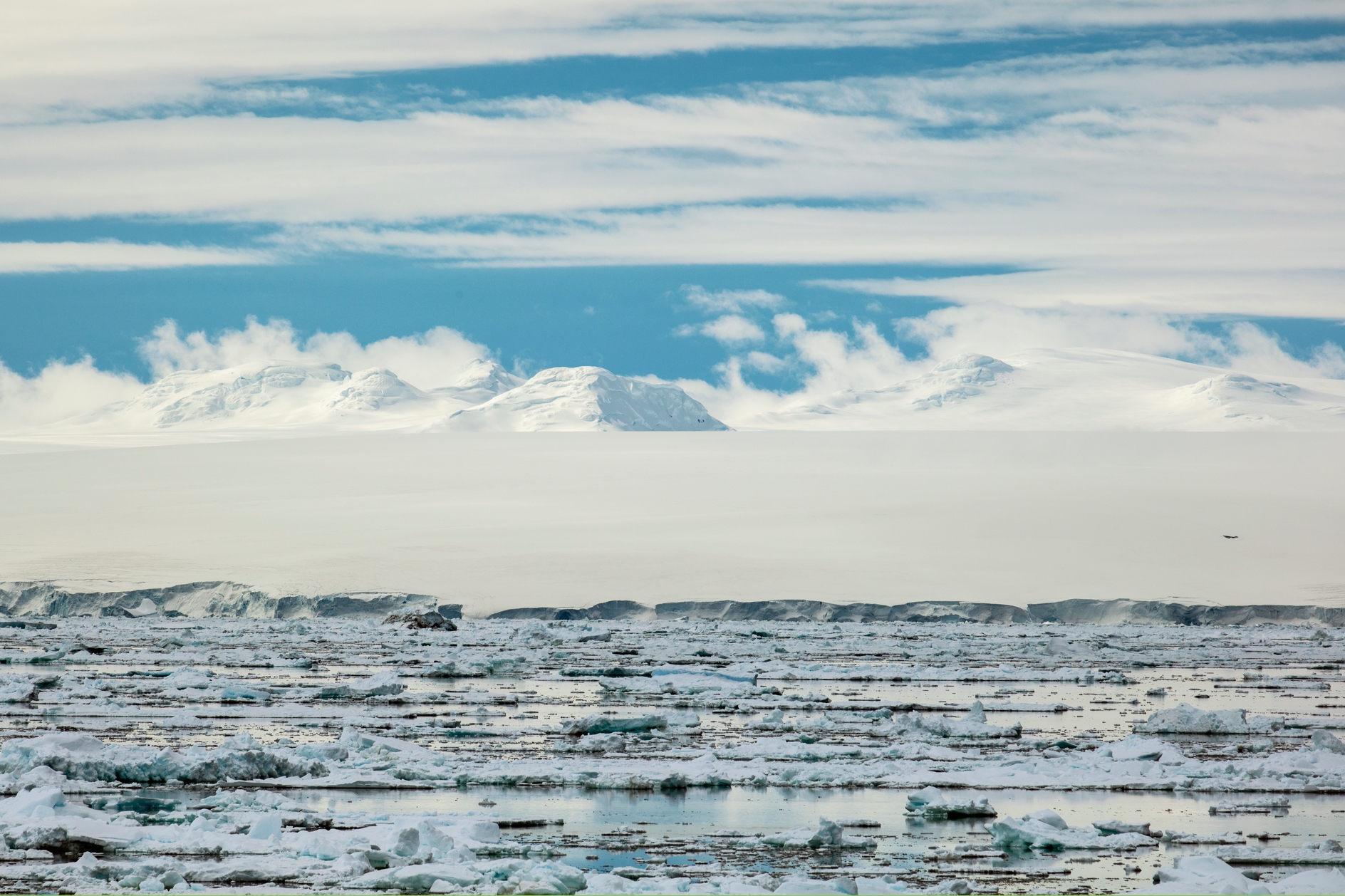
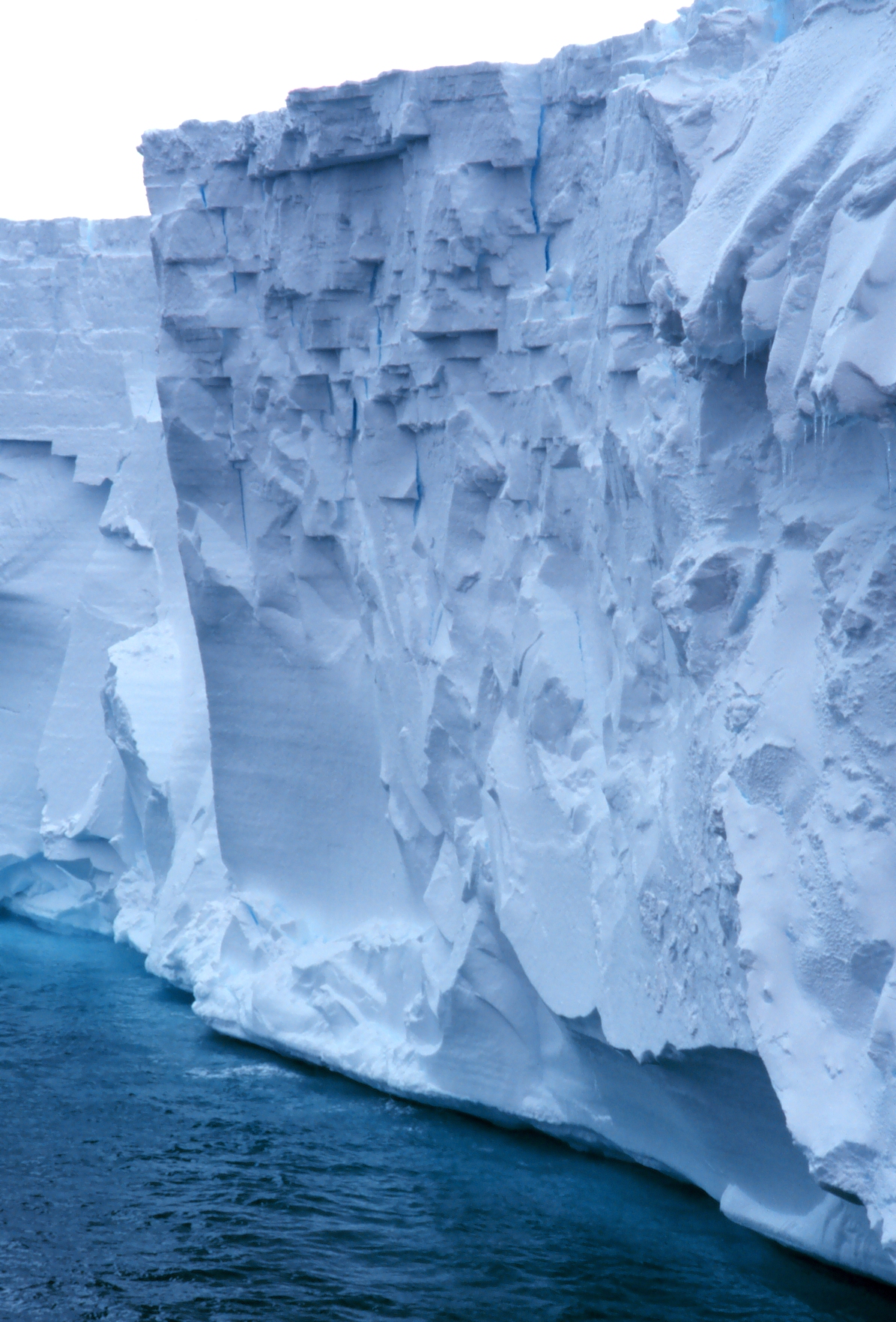
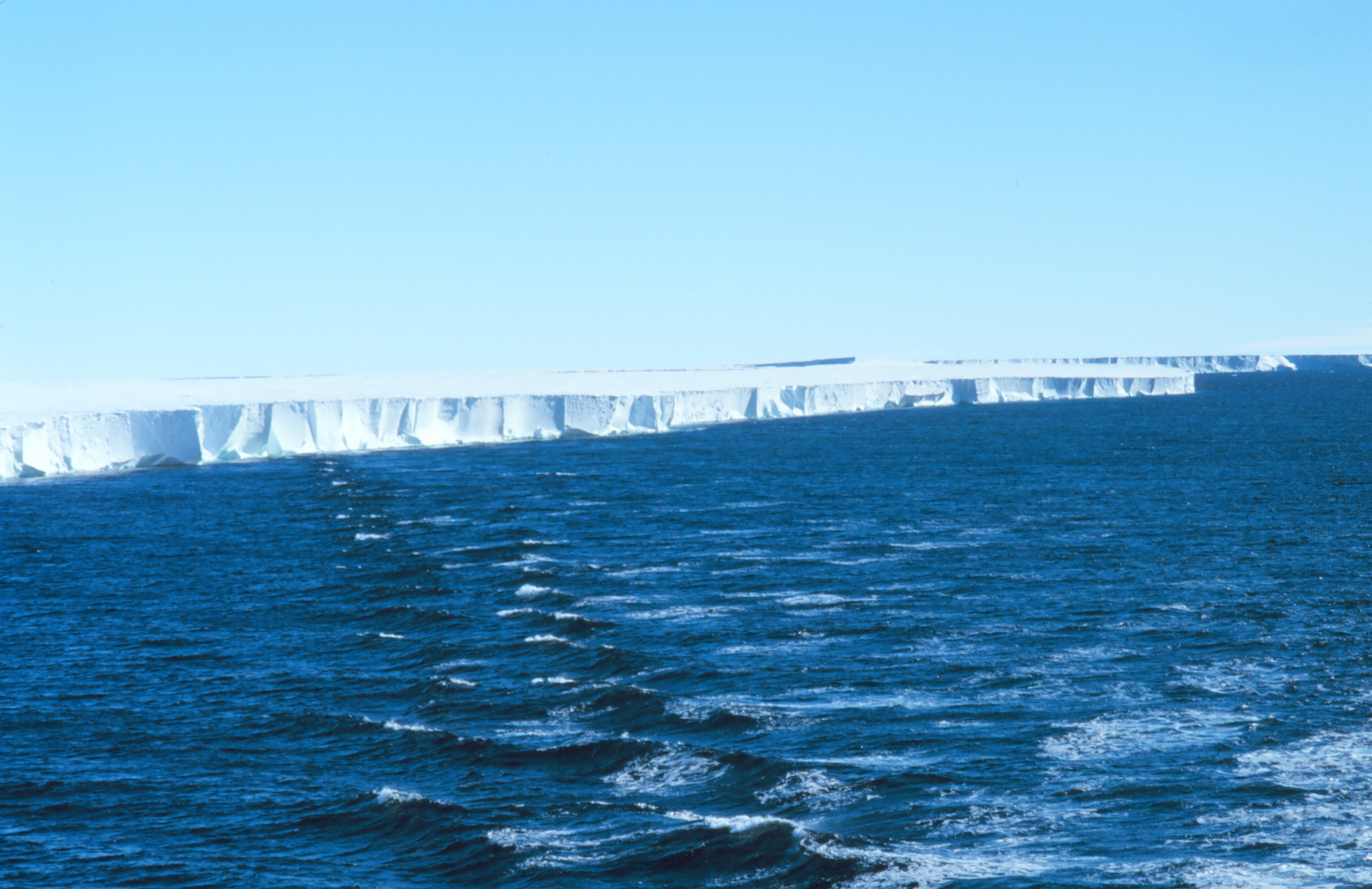
The Antarctic ice wall
It’s simply the edge of an ice platform, and it’s very high and impressive indeed.



The Sun and Moon are local and revolve above the flat Earth
Calculating the distance from the Earth to the Sun using the transit of Venus
We have long known how to calculate the distances between the Earth and the Moon or the Earth and the Sun, which excludes the fact that the Sun and Moon are in the Earth’s sky…
What is a transit of Venus?
A transit of Venus occurs when Venus passes between the Earth and the Sun, appearing as a small black dot that crosses the solar disc. Using the parallax phenomenon, it is possible to calculate the distance between the Earth and the Sun.
What is the parallax effect?
Parallax is the apparent displacement of an object as seen from two different positions. An excellent way of understanding the phenomenon is to hold a finger in front of your eyes and then close one eye, then the other: you’ll see that your finger appears to move in relation to the background. This is the parallax effect.
In astronomy, parallax is used to measure distances: if we observe Venus from two very distant points on Earth, it will appear to pass on slightly different trajectories in front of the Sun.
How can parallax be used to calculate the distance between the Earth and the Sun?
Here’s how to calculate the distance from the Earth to the Sun using the parallax effect:
a) Observing the transit from several points
Astronomers are placed at different locations on Earth, often very far apart (for example, one in Europe, the other in Australia). They precisely time the start and end of Venus’s transit in front of the Sun.
b) Measuring the differences
Depending on where you are observing from, the path followed by Venus on the solar disc appears to be different. This difference is due to parallax and depends on the distance between the two observation points on Earth.
c) Create a giant triangle
We know that the distance between the two observation points on Earth forms the base of a triangle. The angles of this triangle are deduced from the apparent position of Venus as seen from each point. Using simple trigonometric calculations (trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles), we can then deduce the distance from Earth to Venus.
d) Relating the distance from Earth to Venus to the distance from Earth to the Sun
The Earth-Sun distance (known as the astronomical unit, or AU) is proportional to the Earth-Venus distance. These proportions are known thanks to Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Once we know the Earth-Venus distance, all we have to do is apply it to the scale of the solar system.
You will find an extremely detailed explanation of the transit of Venus and the calculation of the distance between the Earth and the Sun in this article :

(Copie of the article : https://web.archive.org/web/20240911042637/https://profmattstrassler.com/articles-and-posts/relativity-space-astronomy-and-cosmology/transit-of-venus-and-the-distance-to-the-sun/)
Conflicting observations
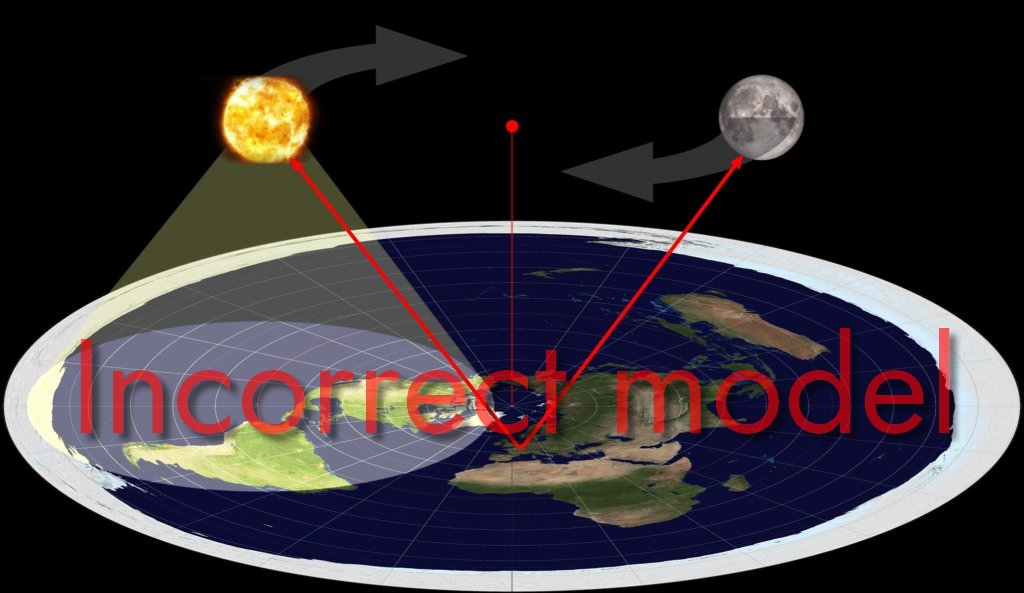
If the Moon and Sun rotated above a flat Earth, then it would be possible to see the Moon and Sun at the same time from anywhere on Earth and at any time of day. However, this is not the case: the Moon and Sun are only visible at the same time at specific times or specific points on the globe.
Moon phases and eclipses are also impossible in such a model.
The Sun and Moon are flat
This hypothesis also contradicts the points made in the previous chapter. Having said that, if the Sun and Moon were flat, we would only see them as a disc when they are directly above us, and when they move away, we would see an ellipse. But this is not the case.

Antarctica is bigger than the Earth
No, Antarctica is not ‘bigger than the Earth’. This argument is sometimes used by proponents of the flat Earth conspiracy theory who claim that the perimeter of Antarctica is 53,510km according to NASA and that the circumference of the Earth is 40,075km according to everyone else, which cannot be true and therefore that we are being lied to and that the Earth is flat.
Well, not only are these figures correct (although not comparable) but they are also entirely possible.
The diagram below is often used by conspiracy theorists:

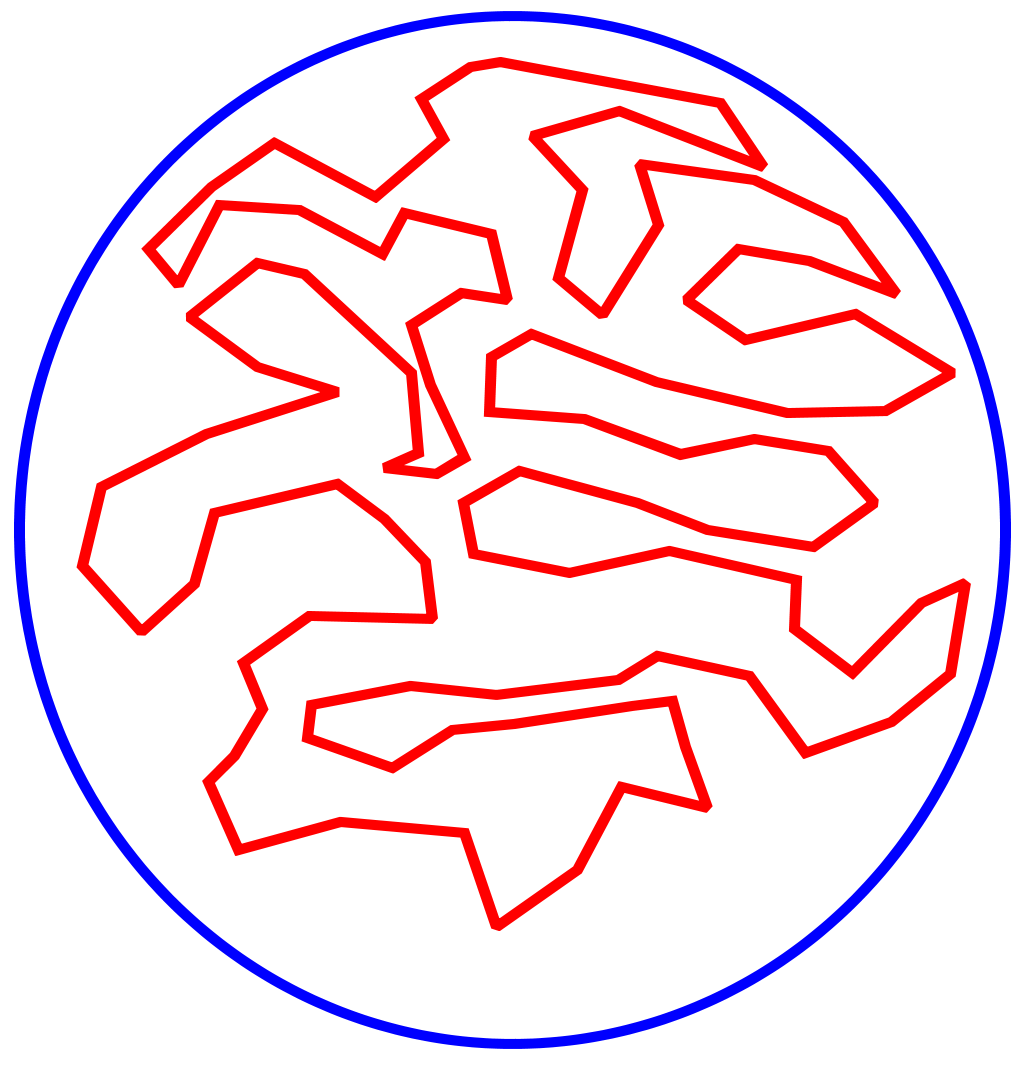
The perimeter of a figure inside a circle of smaller circumference
I don’t think I need to go into this at length, as I think the diagram below shows very clearly that it is perfectly possible to have a geometric figure with a given perimeter in a circle whose circumference is smaller than the perimeter of the figure in question.
The coastline paradox
The last point to consider here, and perhaps the most important, is what is known as the coastline paradox. This paradox is very simple to understand and goes like this:
The coastline paradox is the counter-intuitive observation that the coastline of a landmass has no defined length.
In fact, the more accurately you measure a coastline, the longer it will be. This paradox applies to Antarctica:
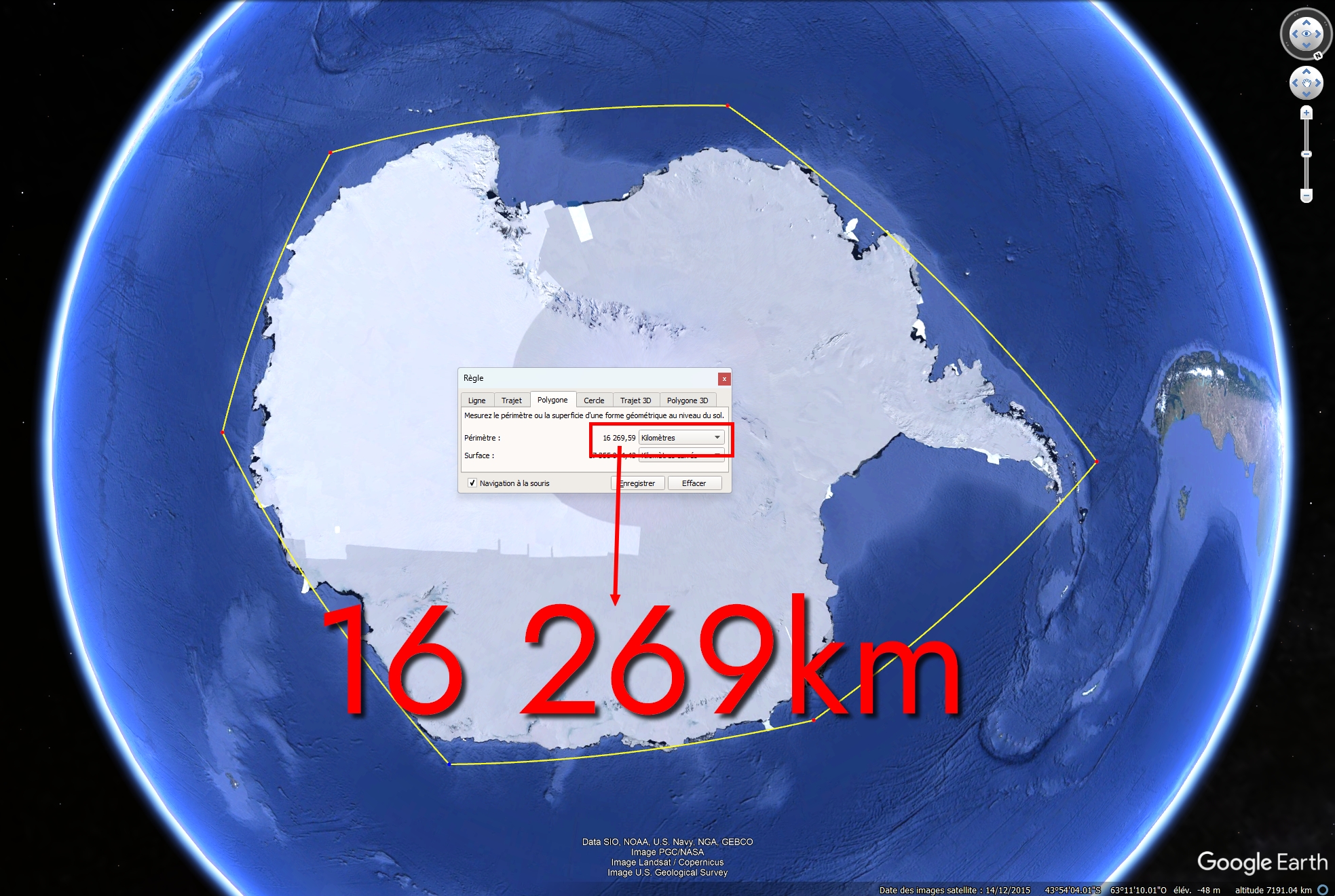
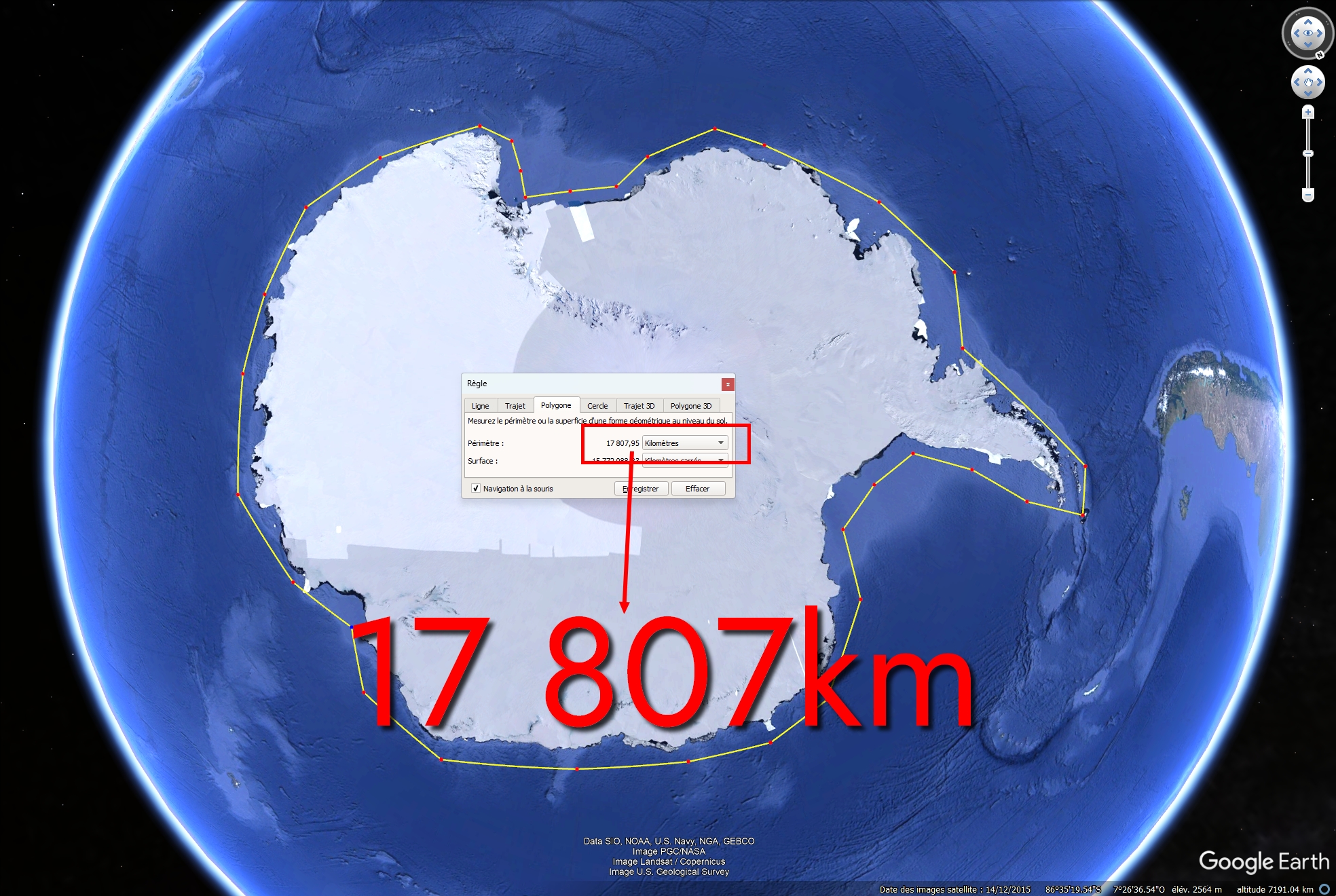
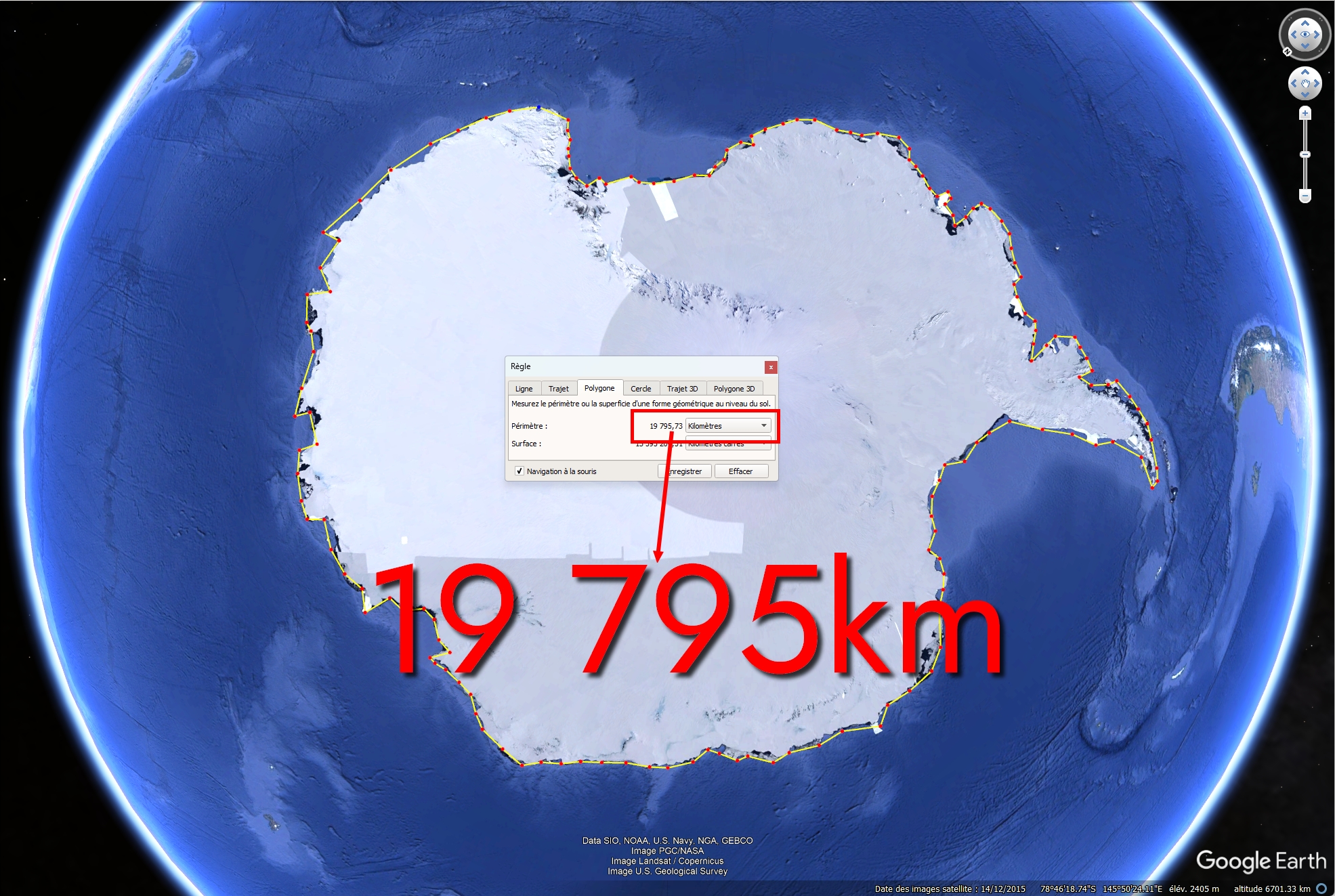
The examples above clearly show the difference in length depending on the precision used to measure the coastline. Now, you can easily imagine the result with a precision of 3.5 million points all around Antarctica…
The result is a perimeter of 53,610km. And if we used 10 million points, we’d get an even bigger value, etc etc.
Government documents admit that the Earth is flat
Conspiracy theorists often use US government documents with the words ‘flat earth’ on them to say ‘the government admits that the Earth is flat’. This reasoning makes absolutely no sense, and here’s why:
- The documents used often come from NASA. NASA is one of the first government agencies to have been able to photograph the Earth and thus see its shape beyond the calculations and demonstrations that proved it irrefutably up until then. It makes no sense to accuse NASA of lying about the shape of the Earth and, at the same time, to think that NASA publishes open-access documents that contradict itself.
- The use of the term ‘Flat Earth’ in these documents is perfectly normal; it is a simplification made in order to reduce the complexity of the calculations that are not necessary in the documents in question. Moreover, in all these documents you will never find the words ‘the Earth is flat’, but turns of phrase such as ‘For the precision required in this document, it is sufficient to treat the surface = O as an ellipsoid whose flattening (ellipticity) is…’ or ‘The model frequently used is that of a flat Earth, with no rotation’. The simple fact of specifying this kind of thing demonstrates that the Earth rotates and is spherical. If this were not the case, NASA would have no need to specify it in these documents…
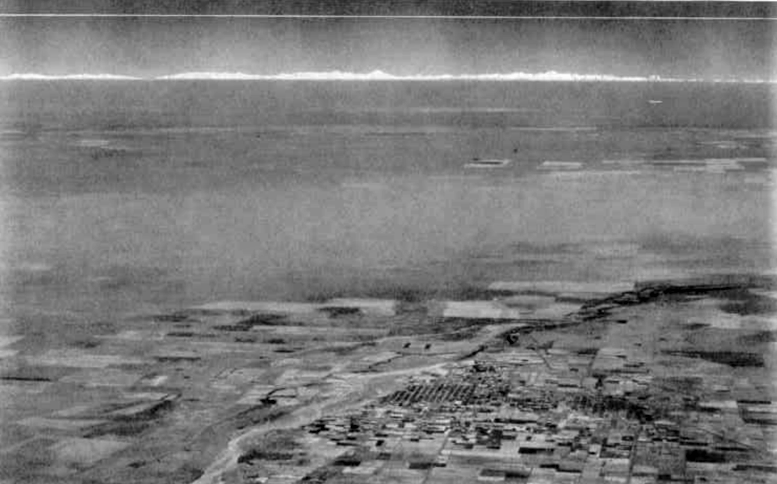

Copy of document : https://web.archive.org/web/20250110103603/https://www.nasa.gov/history/90-years-of-our-changing-views-of-earth/
Examples
Here is an example of the document used. It is clear that a flat Earth model is used here to simplify the calculations, hence the use of the term ‘For the precision required in this document’.


The full document is available below:
Another example :

The full document is available below:
There is plenty of evidence that the Earth is spherical
Planetology
Planetology is the science that studies the formation of planets.
It’s no coincidence that all planets are spherical. We know how planets are formed and why they are round.
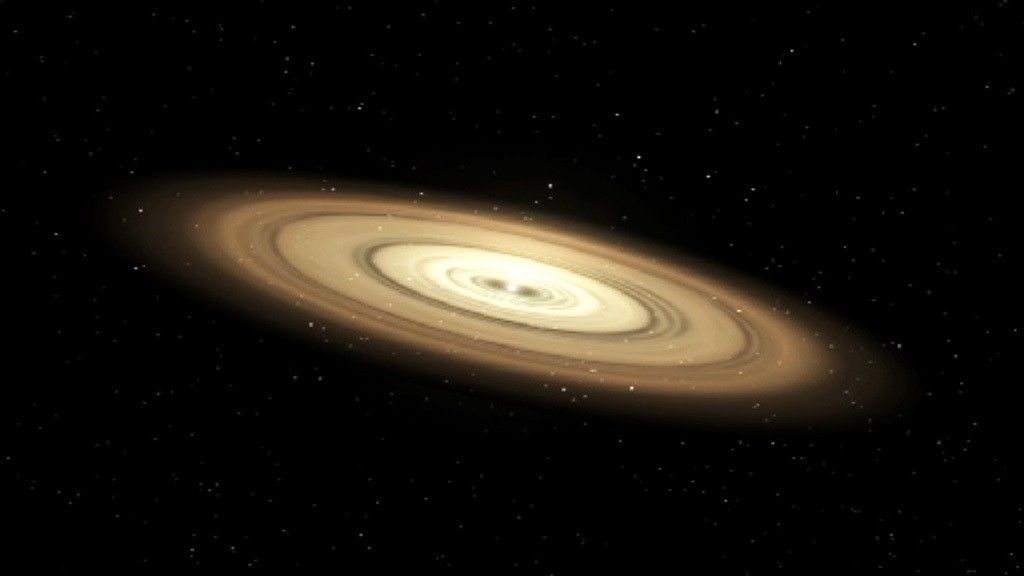

(Copy : How do planets form ?)
You only have to look at all the planets in the solar system to realise that they are all spherical. Why should the Earth be an exception? Knowing how planets are formed, it wouldn’t make sense.
Some conspiracy theorists argue that when we look at other planets, we don’t see a sphere but a disc. This argument makes no sense because :
- If the other planets were flat, we would not systematically see a disc but we could also see an ellipse depending on the orientation of the planet. But this is never the case.

- We can see the planets rotating, so they must be spherical. Below is an accelerated view of the rotation of Mars.

Youtube
Twitter / X
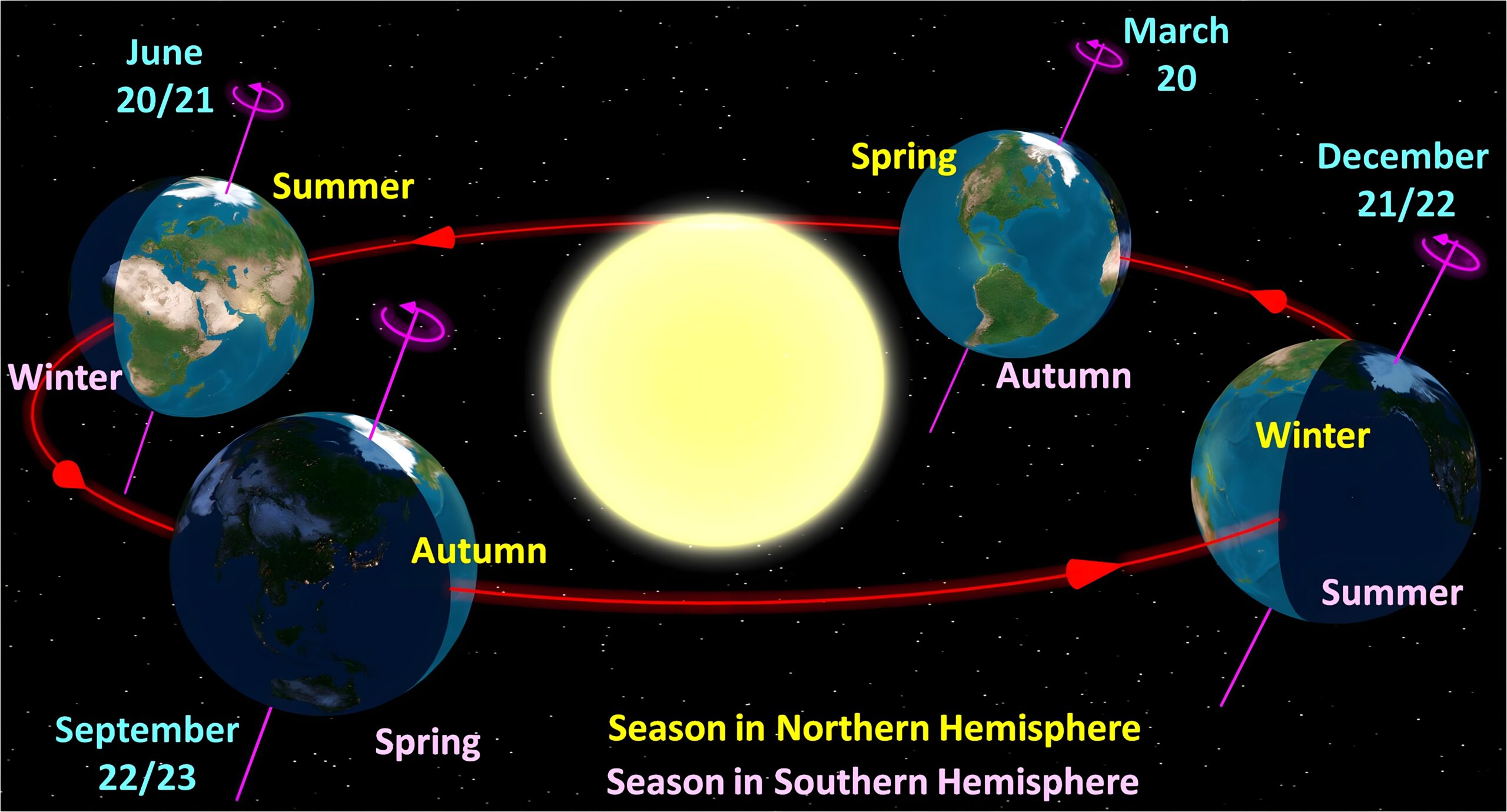
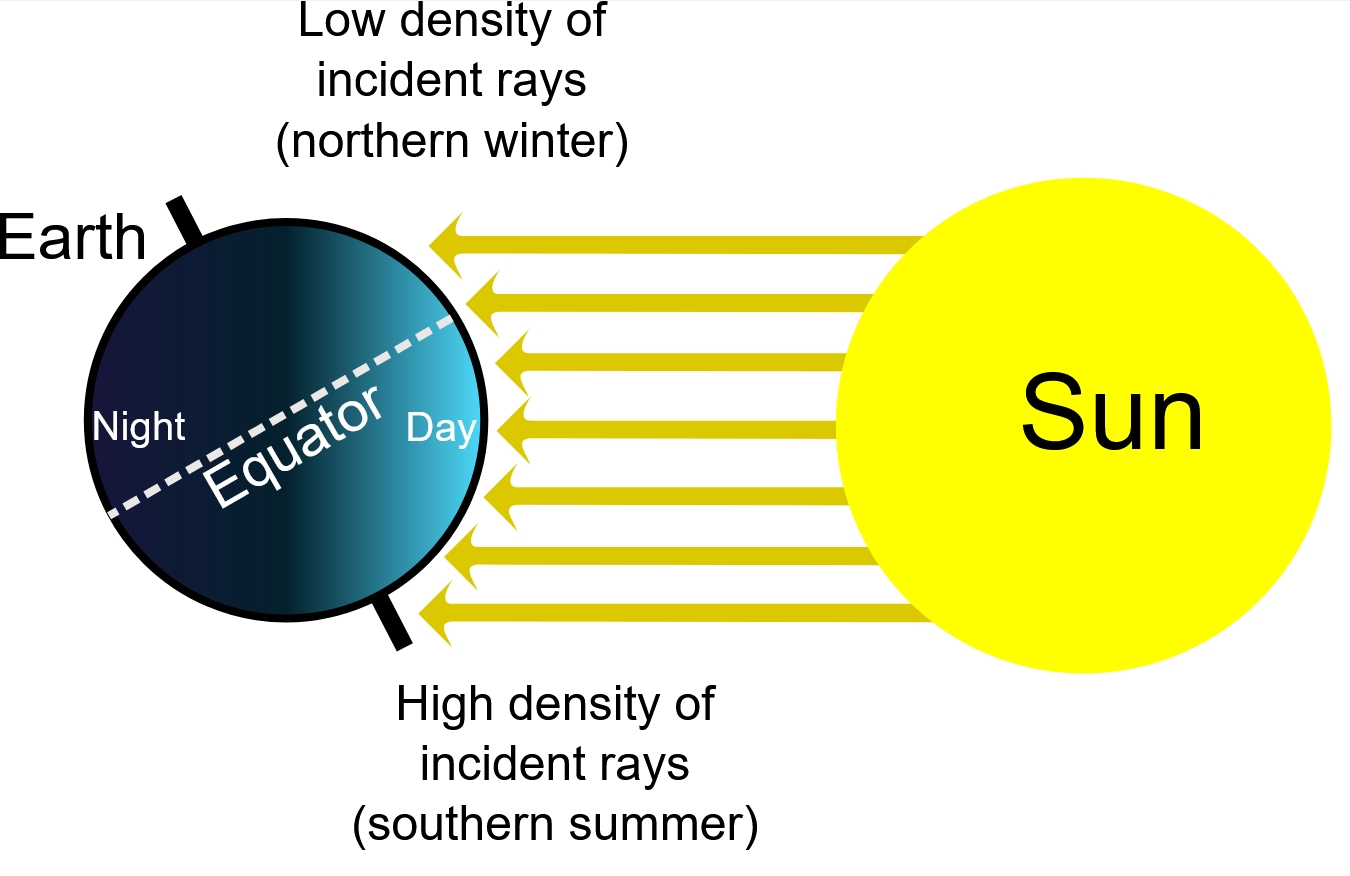
The seasons
Contrary to what you might think, the seasons are not due to the distance between the Earth and the Sun, but to the tilt of the Earth. Depending on its tilt, the poles receive more or less sunlight. This phenomenon of the seasons is not possible on a flat Earth.
Eclipses
Eclipses are not possible on a flat Earth, for fairly obvious reasons…
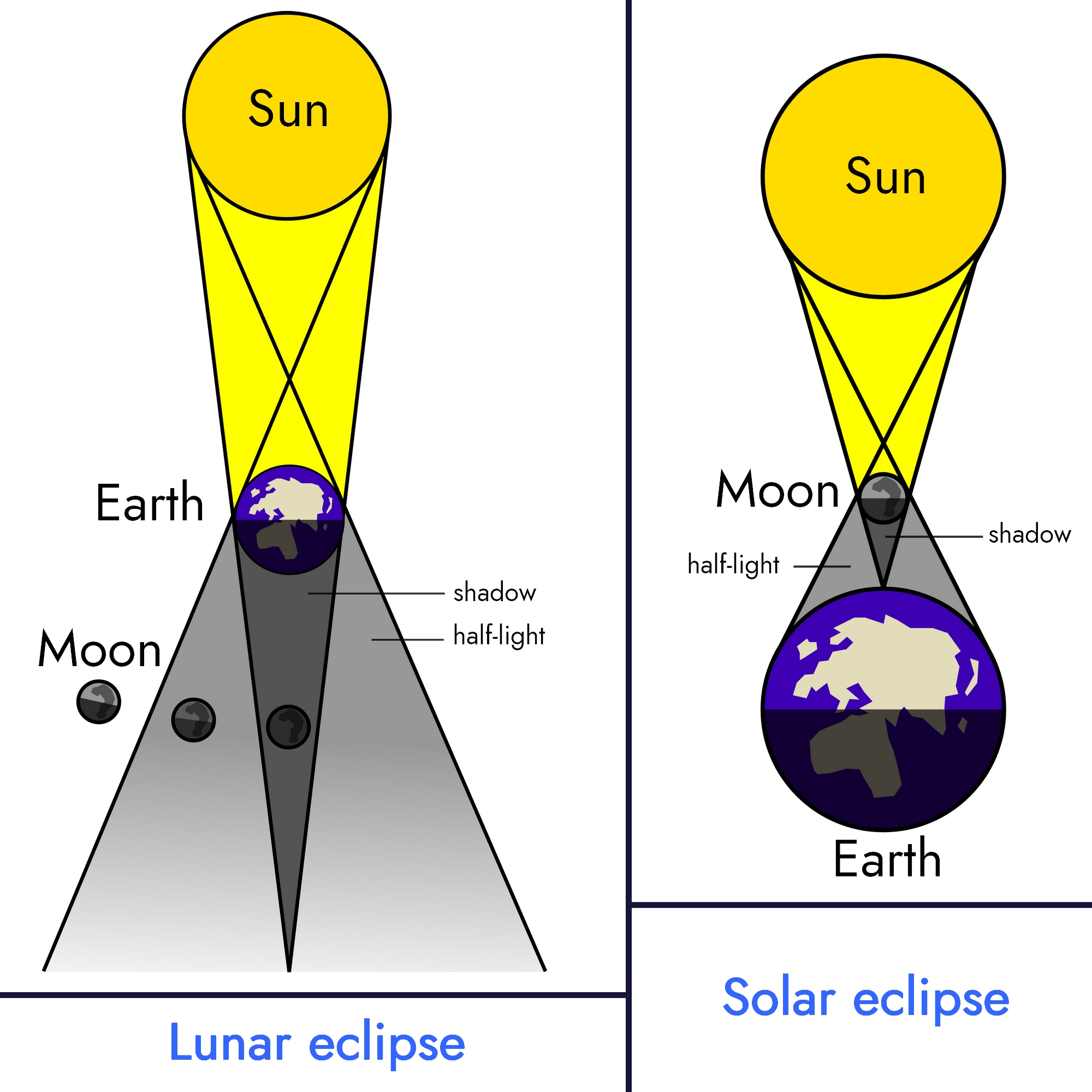
Source diagram 2: Wikipedia
The stars
The fact that the apparent movement of the stars in the sky is not the same depending on whether you are at the equator, in the northern hemisphere or in the southern hemisphere proves that the Earth is not flat.
By taking a timelapse of the starry sky, anyone can see that the stars turn clockwise or anti-clockwise, depending on which hemisphere you are in. In reality, the stars are not moving; this apparent movement is due to the rotation of the Earth on itself.
Satellites
Photographs of the Earth
You can go around the globe
The tides
The sun can be seen for 24 hours in Antarctica
Aviation (flight times)
Comments are closed.





